Ghana on its way to its enhanced child protection system
Ghana on its way to its enhanced child protection system for survivors of child violence
For majority of children in Ghana, violence is an unfortunate part of their everyday life. According to official statistical reports, 9 out of 10 children are exposed to mental or physical violence, and physical punishment is a common phenomenon. More shocking are the figures for sexual violence: one out of five girls is sexually abused. There is an urgent need for action to protect children from violence! For girls and boys who experience and survive violence or abuse, a central, child-friendly centre providing the most essential services under one roof would be established from the first quarter of 2019, where trained personnel from the Social Welfare, Domestic Violence Unit of the Police Service (DOVVSU) and Ghana Health Service are available to offer prompt, secured and confidential service to victims. Our team conducted a technical workshop with representatives of Ministries and other key stakeholders responsible for child protection in Ho, South-East Ghana together with experts from Zanzibar to discuss and develop a roadmap to establish a pilot in Accra. These are the main results at a glance.

Samia Kassid – opening remarks
In November 2017, the World Future Council Foundation invited political decision-makers from 12 African and Asian countries to Zanzibar to acquaint themselves with the country’s comprehensive Children’s Act and its implementation. Zanzibar won the Gold Award of the “Political Oscar” Future Policy Award in 2015.
The Ghanaian delegation, consisting of representatives from the Department of Children of the Ministry of Gender, Children and Social Welfare and the Law Faculty of the Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration were inspired by the one-stop-center model that Zanzibar has currently implemented in 6 out of 11 districts.
What is a one stop center?
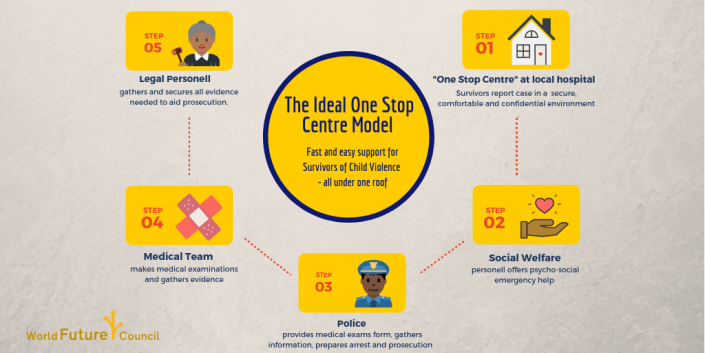
One-Stop-Center (OSC) are central contact points for children and their families affected by (sexualised) violence. Here survivors can find psycho-social support, a police office to initiate criminal investigation as well as medical treatment including collection of forensic evidence under one roof. Ideally, legal help is part of the centre. The graphic illustrates the model:
As an important element of a strong national child protection system, the one-stop-centres provide survivors (girls and boys, women and men) with various initial services under one roof. As a result, the affected person does not have to go through the trauma of narrating the incident several times and also receives quick help. It helps parents stay focused on treating their child and persecuting the perpetrator. In cases without the OSC, survivors mostly have to visit different institutions – that costs money and time and often parents lose the momentum to persue the case. The later a case is reported, the harder it is to gather evidence of abuse on a child’s body.
Ideally, a one-stop center provides four services and is usually docted at a hospital:
- Psycho-social support – this is where the first interview takes place and the social worker decides which further steps are required. If there is an abuse / violence, the child will be escorted to the next room, where a police officer in civilian clothes and trained in child-friendly behaviour will fill in the form to follow up the case.
- Medical examination: in a third room, a medical doctor takes care of the child. Here the first medical and forensic examinations take place. If the child needs further special treatment, it will be treated immediately in the hospital.
- The employees of the one-stop-center are provided by the relevant ministries (Health, Interior, Family Affairs) and the Centre is (at best) coordinated by the Ministry of Health. All employees receive same training so they can better collaborate and follow same procedures and guidelines in writing the reports. This makes it easier for the police and the courts to track and prosecute cases.
- Support for counseling and legal aid is ideally offered in the fourth room.
Ghana on the way to pilot a one stop centre

A member of the Zanzibar team sharing her experience at the workshop

The Director of the Department of Children, speaking at Workshop
After intensive discussions with the Department of Children from April 2018, the World Future Council Foundation organised a technical workshop to fully introduce the state agencies in the establishment and management of a one-stop-center model in Ghana from the 25-27 November 2018. We invited experts from Zanzibar to Ghana: Deputy Chairwoman Halima Abdallah, who spearheaded the establishment of the One-Stop-Center in the Ministry of Family and Health, Dr. Marijani, who has been responsible for medical and forensic investigations since its implementation in 2011, and Farshuu Khalfa, head of a one-stop center in Stone Town. Their insights, expertise and practical experience were most welcome and helpful in drawing up the roadmap for Ghana.
Under the auspices of the Children’s Department, 30 key representatives and decision-makers took part in the workshop to discuss the need for the OSC and to develop the roadmap for a pilot program. The participants represented the Ministry of Health, Ministry of Interior, Ministry of Gender, Children and Social Protection, the Social Welfare Department and the specialised Domestic Violence Unit of the Police service – DOVVSU. Medical representative and international child rights organisations including ActionAid, World Vision, International Needs, UNFPA and UNICEF were also present.
The most important results of the workshop at a glance:
- Development of a roadmap for the establishment of a pilot in Accra
- National coordination agency of the One-Stop-Center pilot program will be the Ministry of Health with support of other ministries
- An inter-ministerial conference is scheduled for the first quarter of 2019 to decide on the roadmap and timetable
- A core group will identify a possible location for the pilot program in Accra

Working groups during the workshops.